Infrared for industrial heating processes

Although using convection heating processes is still very popular, natural gas infrared is a highly advantageous solution for many industrial applications. For example, natural gas infrared can be used to cure finishes and protection layers on metal surfaces, or to dry paper, coatings, inks or fabrics, as well as to cook foods or mould plastics and acrylics.
Why natural gas infrared?
Infrared is a heating method using radiant energy—not absorbed by the air—that is converted to heat when it strikes an opaque object. The absorption of the infrared energy enables rapid evaporation of water and solvents.
There are three categories of infrared:
1. Ceramic or metal fibre matrix
- A premixture of natural gas and air distributed along the fibre burns on the surface.
- The heated fibre emits radiant energy toward the product being processed.
- Heater temperature: between 650 °C and 1,100 °C.
2. Direct-flame burner
- A flame is focused on ceramic plates oriented toward the products being processed.
3. Catalytic
- The natural gas enters at the back of the unit and passes through a pad coated with catalyzer.
- An oxidation-reduction reaction occurs at the front, where oxygen contacts the pad, generating the infrared radiation.
- Heater temperature: between 230 °C and 480 °C
- There is no flame (because the heater temperature is lower than the self-ignition temperature of the natural gas).
Criteria to consider when choosing infrared
The object to be heated can partially absorb or reflect the radiation, or it can transmit it because the radiation also passes through certain substances, such as water and solvents. The energy absorbed is then transferred by conduction throughout the part to be heated.
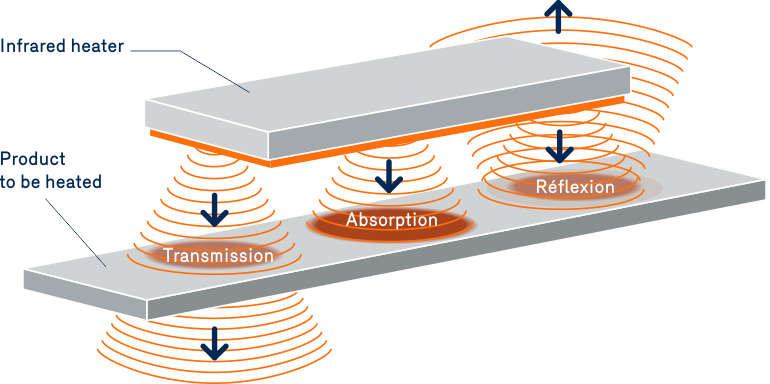
For many applications, it is important to take into account the characteristics of the material to be heated.
For example, the higher a material’s emissivity, the more radiation it can absorb. As well, its colour and finish (matte, satin, gloss) affect the radiation absorption. Given the large variety of materials, coatings, colours and finishes to process, testing different devices is recommended to select the type of heater that produces the best radiation absorption results.
More efficient heating
Infrared heating is often more efficient than convection heating in industrial processes because a greater percentage of the energy input is transferred to the product being heated instead of the oven enclosure and the openings for the parts to enter and leave, a phenomenon which typically results in energy loss.
Furthermore, infrared ovens do not require a long preproduction heat-up time. If the objective is to dry or bake a surface coating, this reduction in the exposure time avoids needlessly heating the mass of the part being processed since the required temperature is reached more quickly.
For drying paint finishes, for example, the radiation enables the part’s heat to be transferred outward, which prevents the formation of a surface skin and bubbles caused by the solvents evaporating, a phenomenon seen with convection ovens.
Examples of industrial processes that benefit from infrared:
- Baking powder-coat finishes (on metal or MDF)
- Drying liquid paint finishes (on metal poles, among other applications)
- Drying water- or solvent-based finishes (on office furniture, for example)
- Cooking or grilling foods
- Moulding plastic products
Better control of heating zones
Since an infrared dryer or oven is equipped with multiple heat lamps, it is easy to divide the oven into several sections, which represents another advantage of infrared over convection. Typically, the parts entering the first section of the oven can be subjected to a high intensity of radiation. Then as they move through the oven, the radiation intensity and temperature can be reduced, allowing for improved product quality. The compartmentalization can also be vertical, based on the geometry of the parts. Generally speaking, having several zones makes it possible to profile the temperature for the process and reduce energy consumption.
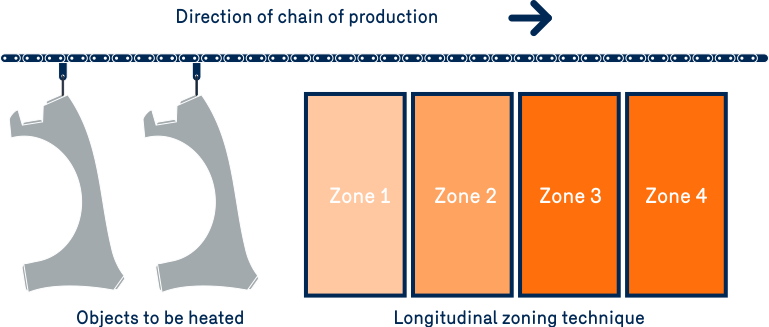
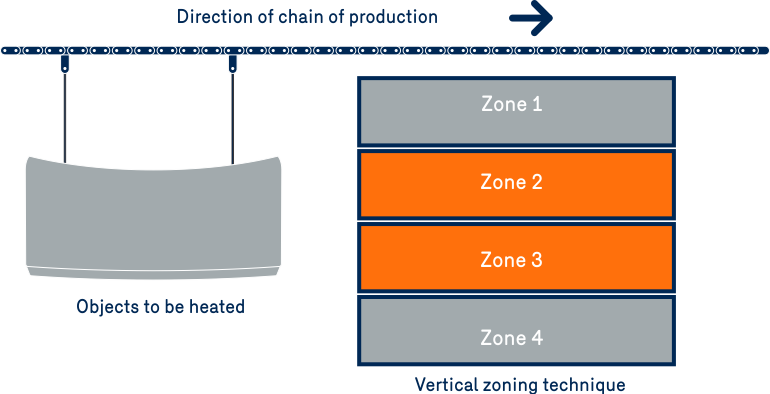
Natural gas infrared heating offers several advantages:
- Less heat emanating into neighbouring work zones
- Lower capital and installations costs
- Less floor space used
- Lower maintenance costs
- Energy savings. Discover 6 more tips for saving energy.
What’s more, Énergir can guide and advise you on the best solution for implementing this technology in your production line. Not to mention the possibility of attractive grants for installing this type of equipment.
To take the next steps, contact our team. You could realize big savings while boosting your productivity!
You may also like...